India stands as a beacon of dynamic economic growth in the global arena, characterized by its vibrant markets and rapidly evolving consumption patterns. As one of the world's largest and fastest-growing economies, it presents a unique blend of traditional values and modern aspirations, which are reflected vividly in the spending habits of its diverse population. From the bustling urban centers like Mumbai to the serene rural heartlands, the nation's consumption patterns offer invaluable insights into its economic pulse and potential future trajectory.
Navigating through India's economic landscape requires a deep understanding of two pivotal aspects: the nuanced consumption behaviors across different societal segments and the intricate dance of inflation rates as guided by astute monetary policies. These elements not only dictate the immediate economic climate but also sculpt the long-term growth and stability of the nation.
This article delves into the depths of India's economic framework, exploring how evolving consumption patterns and strategic inflation management collectively underpin the country's economic resilience and growth. By dissecting historical data alongside current trends, we aim to unveil the complex interplay between consumer behavior, price stability, and policy decisions, providing a comprehensive outlook on India's economic health and its implications for global economic interactions.
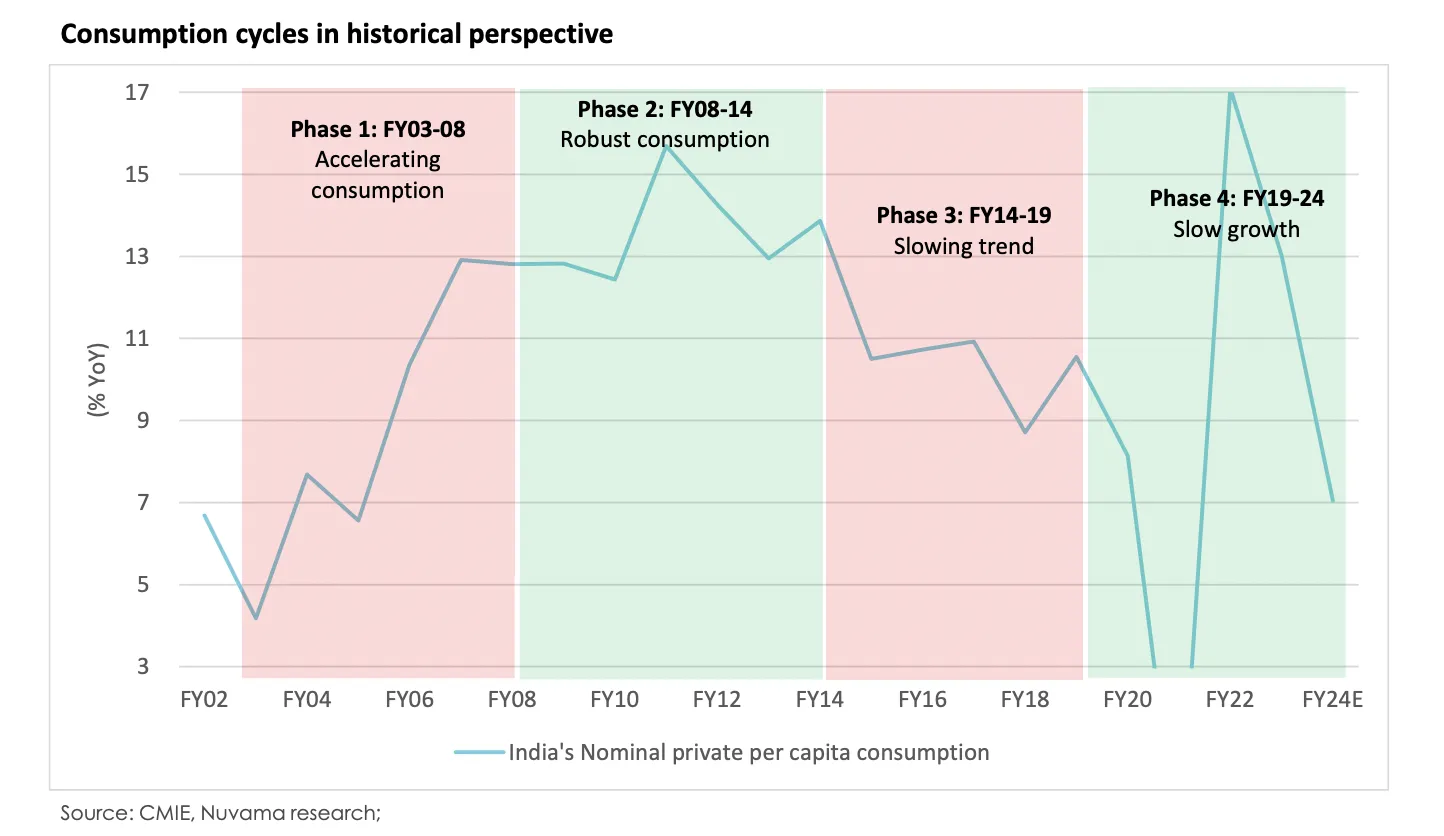
Historical data on India's consumption patterns reveals distinct phases of consumer behavior, significantly shaped by economic conditions and policy changes:
Phase 1 (FY03-08): This period saw accelerating consumption across various sectors, primarily driven by broad-based economic growth and rising incomes. Consumption was robust, reflecting the optimism and financial buoyancy of this era.
Phase 2 (FY08-14): Characterized by robust consumption, even though this period included the global financial crisis (GFC). Fiscal stimuli and government transfers played a crucial role in sustaining consumer spending, particularly at the lower end of the income spectrum.
Phase 3 (FY14-19): Marked a slowdown in consumption growth. Despite moderate growth in incomes, there was an evident shift where high-end consumption began to outpace broader market trends, reflecting growing income disparities.
Phase 4 (FY19-24): Described as a period of slow growth with a K-shaped recovery post-COVID, highlighting stark differences in consumption among different economic groups. This phase saw consumption significantly lagging behind pre-COVID trends, with nominal and real private consumption remaining subdued.
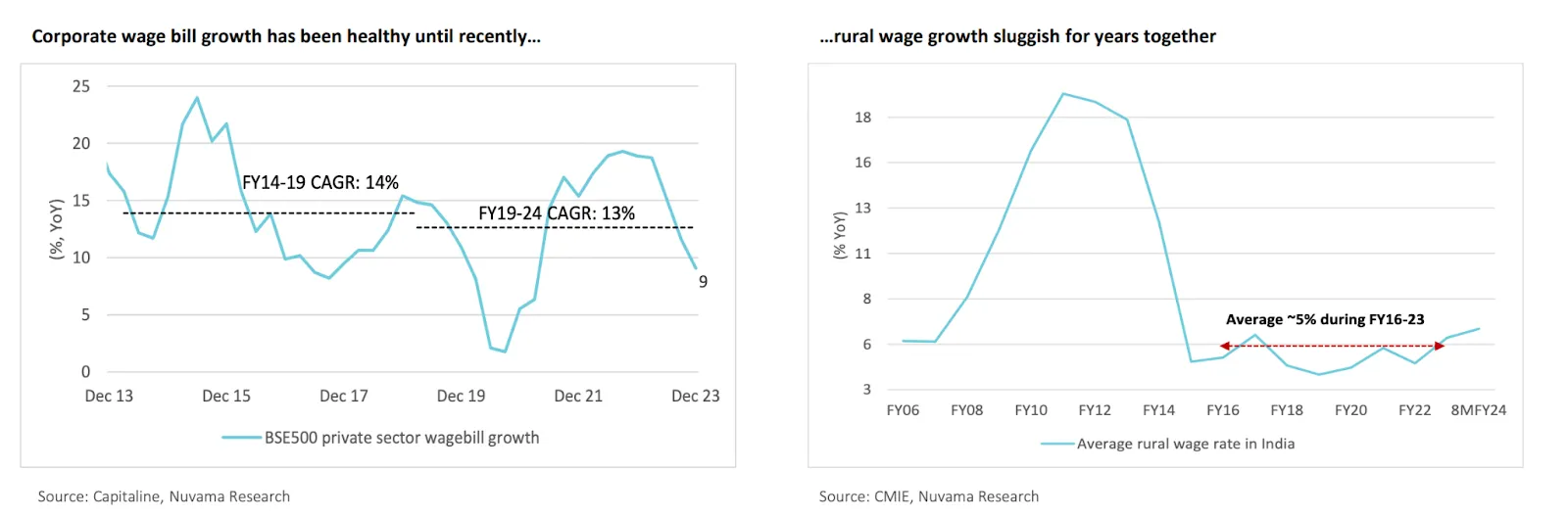
The current trends in India’s consumption are shaped by the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic and the ongoing economic recovery:
Pre-COVID vs. Post-COVID Trends: Consumption patterns have not fully rebounded to pre-COVID levels. As of FY24, private consumption is reported to be approximately 9% below the pre-COVID trend on a nominal basis and 13% below on a real basis. This indicates a cautious consumer environment where spending is still recovering.
Lagging Pre-COVID Trends: Even by FY24, private consumption in India remains below the pre-COVID trend line, both on a real and nominal basis. Specifically, nominal private consumption is approximately 9% below the pre-COVID trend, and real private consumption is about 13% below. This indicates a cautious recovery where consumer spending has not yet fully rebounded to pre-pandemic levels.
Wallet Share Shifts: There have been noticeable shifts in how consumers allocate their spending. The share of spending on food has decreased both in urban (from 44% to 42%) and rural areas (from 56% to 50%), while the share of durables has consistently risen (up approximately 2% to 7% now) across both demographics. This shift may reflect a gradual change in lifestyle and priorities post-pandemic, with an increased focus on long-term investments over daily consumables.
India's inflation landscape has exhibited a dynamic interplay with the Reserve Bank of India's (RBI) monetary policy in recent years. Let's delve into the current trends and the central bank's approach:
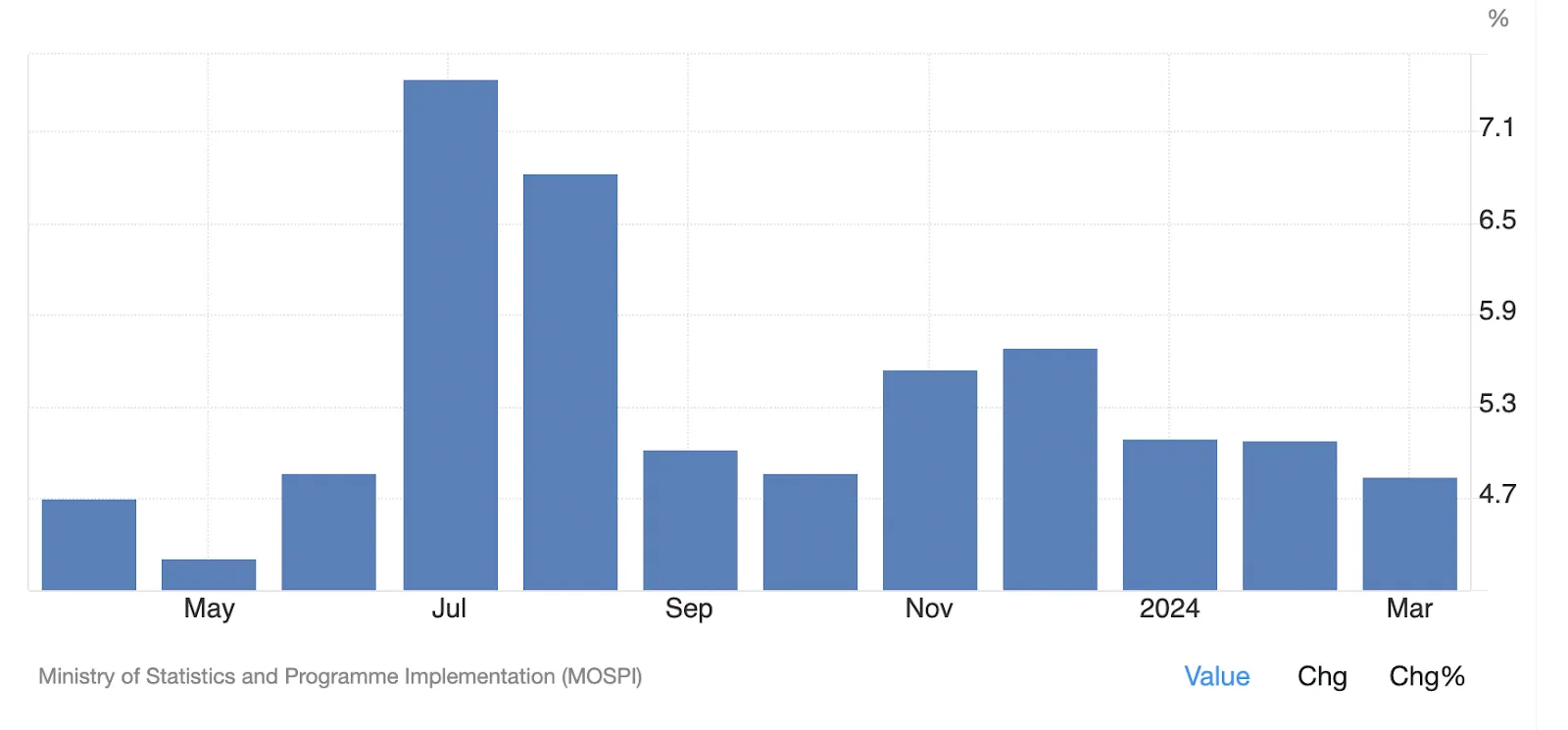
Moderation in CPI: The headline Consumer Price Index (CPI) moderated to 4.9% year-on-year (YoY) in March, down from 5.1% in February. This decline is attributed to a slight easing in food inflation, which decreased marginally from 7.8% to 7.7% YoY, driven by reduced inflation in milk, vegetables, and pulses. Despite these decreases, the inflation rates for pulses and vegetables remain high.
Stable Core CPI: Core CPI, which excludes volatile food and energy prices, remained stable at around 3.3%. This marks the fourth consecutive month where core inflation has stayed below 4%. The fuel and light category showed a significant deflation of 3.2% YoY, contributing to a subdued core inflation rate.
Overall Inflation Outlook: While the headline CPI is now consistently below 5%, and core CPI remains benign under 4%, there are concerns about potential inflationary pressures. These arise from recent increases in crude oil prices and the uncertain trajectory of food inflation, which could push overall inflation higher in the near term.
Inflation Targeting: The RBI follows a flexible inflation targeting framework, aiming for a medium-term target of 4% with a tolerance band of +/- 2%. This framework guides the RBI's monetary policy decisions to maintain price stability and promote economic growth.
Rate Decisions: The RBI's Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) meets bi-monthly to assess inflation and growth dynamics. Based on this assessment, the MPC decides to maintain, increase, or decrease the repo rate, the key interest rate at which the RBI lends to commercial banks. Read this article to understand Interest Rate Cut Expectations In 2024
Recent Stance: In the April 2024 policy meeting, the MPC maintained the repo rate due to the prevailing moderate inflation and the need to support economic growth. However, the RBI remains vigilant and may adjust rates in the future depending on the evolving inflation trajectory.
Balancing Act: The RBI faces the challenge of balancing its inflation target with supporting economic growth, especially in the wake of global uncertainties.
Food Price Management: Managing food price volatility remains crucial to prevent spillover effects on overall inflation.
Communication and Credibility: Effective communication of the RBI's policy stance and its commitment to the inflation target is essential to maintain market confidence and anchor inflation expectations.
India's inflation outlook hinges on various factors , including global developments, domestic food prices, and the RBI's continued adherence to its inflation targeting framework. The coming months will be crucial to observe how the interplay between these forces shapes India's inflation trajectory and the RBI's monetary policy response.
India's economic landscape currently presents a picture of optimism tempered by caution. Let's explore the key factors shaping the outlook and the implications for corporate earnings :
Strong GDP Growth: India is projected to be the fastest-growing major economy globally in 2024, with estimates ranging from 6.4% to 7.2%. This robust growth is driven by factors like:
Robust Domestic Demand: Rising consumer confidence and government spending on infrastructure are fueling domestic consumption and investment.
Manufacturing Push: Initiatives like "Make in India" are encouraging domestic manufacturing, potentially boosting exports and creating jobs.
Favorable Demographics: India's young and growing population presents a vast consumer base and workforce, fostering long-term economic potential.
Inflationary Pressures: While overall inflation is within the RBI's tolerance band, food inflation remains a concern. Rising global commodity prices and supply chain disruptions could further exacerbate inflationary pressures.
Geopolitical Uncertainty: The ongoing global conflict and associated economic sanctions have the potential to disrupt trade and impact India's economic stability.
Interest Rate Environment: The RBI's future monetary policy decisions, particularly regarding potential interest rate hikes, could impact corporate borrowing costs and investment activity.Read this article to understand Interest Rate Cut Expectations In 2024
Healthy Profit Growth: Earnings growth for Indian stock markets is expected to be muted in Q4 FY24 , compared to the strong performance for corporate India over the first 9 months of FY24. The Nifty is projected to grow by 5% YoY, with profit margins shrinking. Sectors like autos, consumer services, and private banks are expected to see strong growth, while IT, FMCG, and metals are facing headwinds.
Valuation Concerns: However, some analysts express concerns about stretched valuations in certain sectors. Rising interest rates could put pressure on future earnings growth, potentially leading to a correction in stock prices.
Focus on Profitability: Companies are expected to prioritize cost optimization and operational efficiency to sustain profit margins in the face of potential headwinds.
Overall, India's economic outlook is cautiously optimistic. While strong domestic fundamentals support near-term growth, managing inflation and navigating global uncertainties remain key challenges. Corporate earnings are expected to grow, but valuations might need to adjust to reflect evolving economic conditions.
As we reflect on the intricate tapestry of consumption and inflation trends in India, it becomes evident that the nation's economic resilience is deeply embedded in its ability to adapt and transform. The dynamic interplay between traditional market behaviors and modern economic responses has not only shaped the current economic framework but also paved the way for future growth and stability.
India's journey through various economic phases — marked by robust growth, periods of crisis management, and ongoing recovery for largecaps , smallcaps & midcapsfrom the COVID-19 pandemic — illustrates a remarkable capacity to maintain stability and foster growth despite global and domestic challenges. The resilient consumption patterns across diverse demographics highlight an inherent strength of the Indian market: its vast and varied consumer base equipped to adjust in times of adversity.
Moreover, the strategic management of inflation through vigilant monetary policies by the Reserve Bank of India underscores a committed approach to sustaining economic stability. The RBI’s efforts to balance growth with inflation control reflect a nuanced understanding of the broader economic implications of price stability.
As global observers and stakeholders within the Indian economy, the insights gained from analyzing these trends are invaluable. They not only offer a lens to view India's economic resilience but also provide a blueprint for navigating future uncertainties. The lessons learned from India's management of consumption dynamics and inflation pressures are applicable worldwide, offering strategies for fostering resilience in diverse economic landscapes.
Moving forward, the ability of India to continue adapting its economic policies and consumption behaviors in response to changing global conditions will be crucial. Stakeholders, from policymakers to businesses, must remain agile and proactive, harnessing the power of data-driven insights and innovative strategies to thrive in an evolving economic environment.
In conclusion, India’s economic resilience, as demonstrated through its management of consumption and inflation, serves as a beacon of strategic adaptability and growth potential. For those engaged with or interested in the dynamics of emerging markets, staying attuned to these trends will be key to understanding and leveraging opportunities in India’s vibrant economy.
Discover investment portfolios that are designed for maximum returns at low risk.
Learn how we choose the right asset mix for your risk profile across all market conditions.
Get weekly market insights and facts right in your inbox
It depicts the actual and verifiable returns generated by the portfolios of SEBI registered entities. Live performance does not include any backtested data or claim and does not guarantee future returns.
By proceeding, you understand that investments are subjected to market risks and agree that returns shown on the platform were not used as an advertisement or promotion to influence your investment decisions.
“I was drawn to Wright Research due to its multi-factor approach. Their Balanced MFT is an excellent product.”

By Prashant Sharma
CTO, Zydus
By signing up, you agree to our Terms and Privacy Policy
“I was drawn to Wright Research due to its multi-factor approach. Their Balanced MFT is an excellent product.”

By Prashant Sharma
CTO, Zydus
Skip Password
By signing up, you agree to our Terms and Privacy Policy
“I was drawn to Wright Research due to its multi-factor approach. Their Balanced MFT is an excellent product.”

By Prashant Sharma
CTO, Zydus
“I was drawn to Wright Research due to its multi-factor approach. Their Balanced MFT is an excellent product.”

By Prashant Sharma
CTO, Zydus
Log in with Password →
By logging in, you agree to our Terms and Privacy Policy
“I was drawn to Wright Research due to its multi-factor approach. Their Balanced MFT is an excellent product.”

By Prashant Sharma
CTO, Zydus
Log in with OTP →
By logging in, you agree to our Terms and Privacy Policy
“I was drawn to Wright Research due to its multi-factor approach. Their Balanced MFT is an excellent product.”

By Prashant Sharma
CTO, Zydus
Answer these questions to get a personalized portfolio or skip to see trending portfolios.
Answer these questions to get a personalized portfolio or skip to see trending portfolios.
(You can choose multiple options)
Answer these questions to get a personalized portfolio or skip to see trending portfolios.
Answer these questions to get a personalized portfolio or skip to see trending portfolios.
Answer these questions to get a personalized portfolio or skip to see trending portfolios.
(You can choose multiple options)
Investor Profile Score
We've tailored Portfolio Management services for your profile.
View Recommended Portfolios Restart