The Indian economy relies heavily on the infrastructure industry. This sector is critical to India's overall growth, and the government has placed a high priority on enacting regulations that would assure the country's building of world-class infrastructure promptly. Infrastructure improvement projects can be supported in various ways, including publicly, privately, or through public-private partnerships. In terms of economics, infrastructure frequently entails the creation of public goods. As a result, infrastructure is commonly financed, controlled, supervised, or regulated by the government, either entirely or partially.
1. Infrastructure & Economic Growth Have a Relationship
Economic growth and infrastructure have a two-way relationship. One, infrastructure encourages economic growth, and two, infrastructure changes due to economic expansion. Infrastructure is the foundation upon which economic growth is built. It includes those services that aid the development of directly productive activities.
Infrastructure outputs, such as power, water, and transportation, are used as inputs in the directly productive sectors, such as agriculture and manufacturing. As a result, the limited availability of the former leads to inefficient asset utilization in the latter. Infrastructure improvement, such as transportation, has a significant impact on productivity. Thus, infrastructure is the cornerstone of modern technology in almost every area.
Infrastructure should be sustainable, robust, and inclusive in order to have the maximum influence on boosting economic recovery in the short term and long-term stability. This type of transformational infrastructure has the potential to benefit everyone. Good Infrastructure outcome is undoubtedly an example of a factor that influences the positive effect of the investment.
1.1 Infrastructure Types
Soft Infrastructure: This sort of infrastructure usually ensures seamless operation and is less capital intensive, relying instead on human capital to provide service. The healthcare system, financial institutions, governmental systems, law enforcement, and educational systems are all examples of this.
Hard Infrastructure refers to the physical structures that allow entities to manage a contemporary, industrialized country. Roads, highways, bridges, and the capital and assets required to operate and maintain them are examples.
Critical Infrastructure: As the name implies, critical infrastructure comprises facilities such as energy, power, telecommunications, public health, and agriculture, among other things.
Budget Expectations From The Infra Sector
The infrastructure sector is expected to be in the spotlight ahead of the Union Budget for 2022-23, with some significant announcements in the pipeline. However, there are some existing moves by the government that need to be taken into account and few expectations from the infrastructure sector.
To assist India to become a manufacturing hub and more competitive globally, the government has proposed an ambitious plan to invest Rs 111 trillion through the National Infrastructure Pipeline and other programs such as 'Make in India' and Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes.
The government should focus on Capex allocation for more than 80% of complete projects. In addition, interventions are needed to improve and diversify infrastructure financing sources to witness a multiplier effect. In this context, it is advised that the government consider developing the municipal bond market to allow urban local governments to raise cash for infrastructure investment.
More focus should be paid to attract private investment for the National Monetisation Pipeline to build a favorable regulatory framework, a transparent bidding process, flexible contract management, and a credible dispute resolution method. In addition, tax incentives for infrastructure investment trusts were sought, and the NITI Aayog's recommendation was implemented to put them under the NIP.
2.1 Themes & Ways to Invest in The Infra Sector?
As it has been established that the infrastructure sector will be in the spotlight, it is evident that significant companies from this industry can provide superior returns.
The easiest way to track if the infra industry is performing well is to look at the Nifty Infra Index. Companies in the NIFTY Infrastructure Index provide telecom, power, port, air, roads, railways, shipping, and other utility services. The Index includes a maximum of 30 publicly traded companies on the National Stock Exchange of India (NSE).
The NIFTY Infrastructure Index is calculated using the free-float market capitalization approach, with the index's level using the free-float market capitalization method.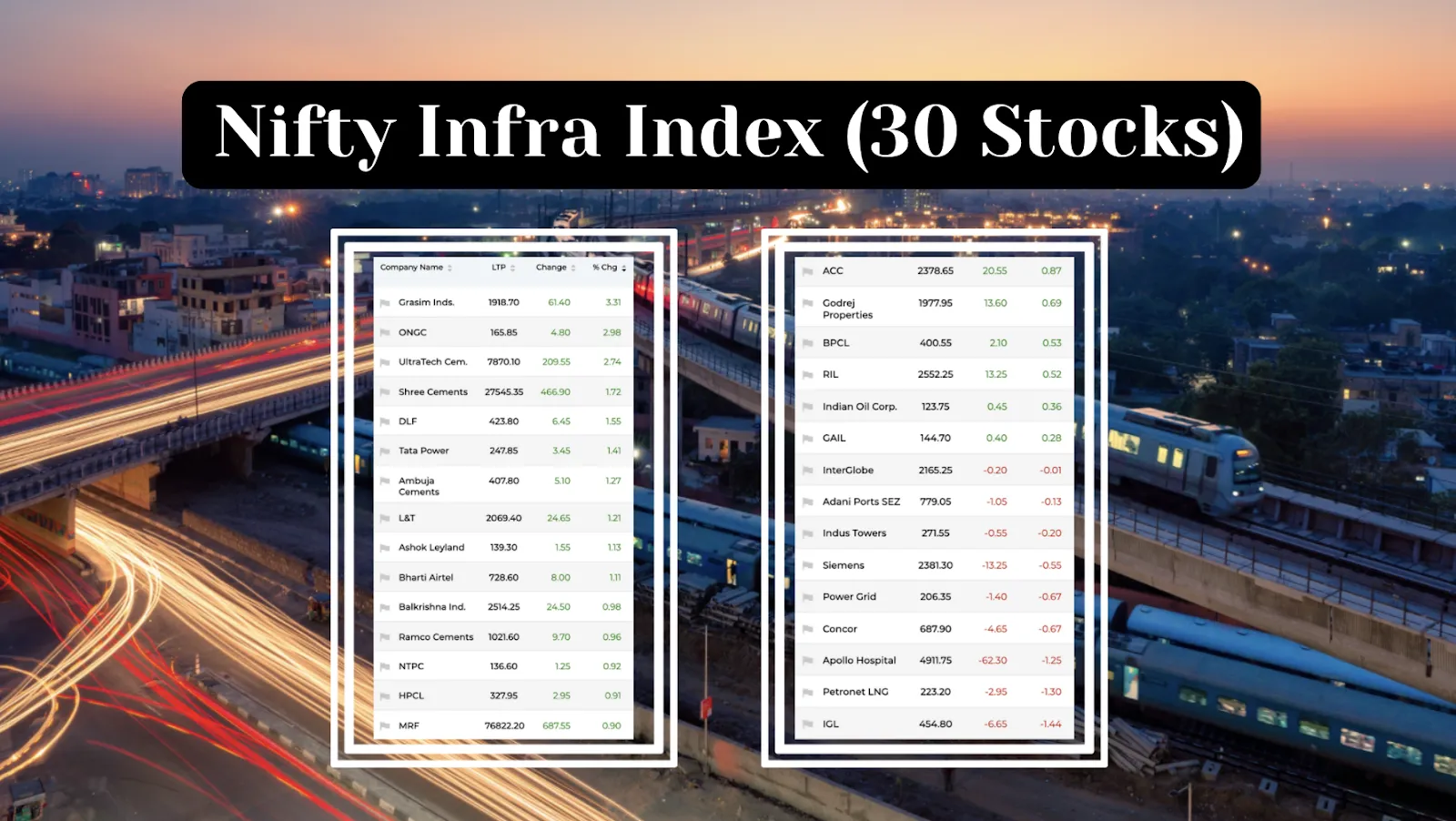

2.2 Factors to Consider When Evaluating Investments in The Infrastructure Industry?
Examine any debt owned by these corporations, as infrastructure development is a capital-intensive process that necessitates ongoing financial infusion. In addition, because infrastructure firms are usually involved in the building or development of any project, it is necessary to evaluate their order book or deal pipeline to determine revenue visibility and cash flows.
Examine the regulations around the projects, as many are either partially controlled by the government or are subject to stringent government regulations. A more flexible regulatory system is preferable since it allows enterprises more flexibility in managing projects and finances.
Examine the company's return ratios, such as operating profit margins and return on capital employed (ROCE). To determine the size of the order book and the revenue visibility it provides, look at the order book/revenue ratio. This ratio should be more prominent, but only if the company can meet its responsibilities.
Q. Is Funding for Infra Still a Constraint for GOI?
Last year, the budget raised CAPEX by 26%, bringing spending to Rs 5.5 lakh crore. This year, we forecast a 25% growth in capital spending, bringing Rs 7 lakh crore. PSUs and supplementary budgetary resources typically contribute an additional Rs 2 lakh crore. The newly established National Bank will contribute another Rs 2 lakh crore For Financing Infrastructure and Development.
Thus, funding is no longer a barrier to infrastructure development in the country, and the focus must now move to project availability.
In addition, the government must begin planning for the next generation of big infrastructure projects. These could take the shape of bullet trains, ports, roads, hydroelectric projects, or infrastructure projects.
According to a recent assessment, India will require a staggering Rs 50 trillion (US$ 777.73 billion) in infrastructure by this year to achieve sustainable development. It also highlights a variety of investment prospects for international investors in the country's infrastructure development.
Given the current market situation, the Indian government aims to spend USD 1.4 trillion on infrastructure between 2019 and 2023, with a $ 750 billion investment in railway infrastructure by 2030. On the other hand, the advent of the pandemic put infrastructure corporations in a difficult position to recover from an all-time low reached the previous year. This necessitates the development of highly effective tactics to boost the sector's growth.
The government had allocated Rs. 233,083 crore (US$ 32.02 billion) to improve transportation infrastructure in the Union Budget 2021. The government has increased the number of projects in the 'National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP)' to 7,400. As of 2020, 217 projects totaling Rs. 1.10 lakh crore (US$ 15.09 billion) had been completed. As of July 2021, the government had invested US$1.4 trillion in infrastructure development through the NIP.
Discover investment portfolios that are designed for maximum returns at low risk.
Learn how we choose the right asset mix for your risk profile across all market conditions.
Get weekly market insights and facts right in your inbox
It depicts the actual and verifiable returns generated by the portfolios of SEBI registered entities. Live performance does not include any backtested data or claim and does not guarantee future returns.
By proceeding, you understand that investments are subjected to market risks and agree that returns shown on the platform were not used as an advertisement or promotion to influence your investment decisions.
"I was drawn to Wright Research due to its multi-factor approach. Their Balanced MFT is an excellent product."

By Prashant Sharma
CTO, Zydus
By signing up, you agree to our Terms and Privacy Policy
"I was drawn to Wright Research due to its multi-factor approach. Their Balanced MFT is an excellent product."

By Prashant Sharma
CTO, Zydus
Skip Password
By signing up, you agree to our Terms and Privacy Policy
"I was drawn to Wright Research due to its multi-factor approach. Their Balanced MFT is an excellent product."

By Prashant Sharma
CTO, Zydus
"I was drawn to Wright Research due to its multi-factor approach. Their Balanced MFT is an excellent product."

By Prashant Sharma
CTO, Zydus
Log in with Password →
By logging in, you agree to our Terms and Privacy Policy
"I was drawn to Wright Research due to its multi-factor approach. Their Balanced MFT is an excellent product."

By Prashant Sharma
CTO, Zydus
Log in with OTP →
By logging in, you agree to our Terms and Privacy Policy
"I was drawn to Wright Research due to its multi-factor approach. Their Balanced MFT is an excellent product."

By Prashant Sharma
CTO, Zydus
Answer these questions to get a personalized portfolio or skip to see trending portfolios.
Answer these questions to get a personalized portfolio or skip to see trending portfolios.
(You can choose multiple options)
Answer these questions to get a personalized portfolio or skip to see trending portfolios.
Answer these questions to get a personalized portfolio or skip to see trending portfolios.
Answer these questions to get a personalized portfolio or skip to see trending portfolios.
(You can choose multiple options)
Investor Profile Score
We've tailored Portfolio Management services for your profile.
View Recommended Portfolios Restart