by Naman Agarwal
Published On Sept. 3, 2025
Volatile market conditions can be nerve-wracking for both new and experienced traders, especially when every news headline seems to move prices dramatically. In such markets, option strategies that balance profit potential with defined risk like the bull call spread offer a smart way to participate in upward trends while managing the dangers of unpredictable swings. This blog explains how the bull call spread works, its advantages and disadvantages, and how traders can best use it when markets are choppy.
A bull call spread is an options trading strategy involving two call options with the same expiry but different strike prices. Here’s how it works:
Buy one at-the-money (lower strike) call option.
Sell one out-of-the-money (higher strike) call option. Both options should have the same expiration date. The goal is to profit from a moderate rise in the price of the underlying asset while limiting your maximum loss to the net premium paid for the spread.
Pros
Limited Risk: The maximum loss is restricted to the net premium paid, offering peace of mind even in highly volatile markets.
Lower Relative Cost: Premium paid is reduced, thanks to selling the higher strike call, making it more affordable than buying a single call.
Defined Reward: You know the maximum profit potential from the start.
Cons
Limited Profit: Unlike a standalone call, the profit is capped because gains beyond the sold strike are foregone.
Requires Moderate Bullishness: Works best when the market rises slightly; a larger rally means missing out on extra profits.
Complexity: Slightly more complex than buying a single option.
In volatile environments, option premiums become expensive due to higher implied volatility. The bull call spread counteracts this by selling a call option to offset part of the cost. Unlike singular call buying, this strategy lowers break-even and risk, making it ideal when expecting a moderate upward move with controlled downside. It’s especially popular among Indian traders who wish to participate in rallies without overcommitting capital or risking large losses.
Aspect | Bull Call Spread | Single Call Option |
Premium Cost | ||
Breakeven Point | ||
Maximum Profit | Limited, difference between strikes – net premium | |
Maximum Loss | ||
Margin Requirement | ||
Best Market Scenario | ||
Impact of Volatility |
To calculate the outcomes for a bull call spread:
Net Premium Paid = Cost of long call - Premium received from short call.
Maximum Profit = (Higher strike price – Lower strike price) – Net premium paid.
Maximum Loss = Net premium paid.
Breakeven Point = Lower strike price + Net premium paid.
For example, if Nifty is at 19,000:
Buy 19,000 Call at ₹100
Sell 19,500 Call at ₹30
Net premium = ₹100 – ₹30 = ₹70
Maximum profit = (19,500 – 19,000) – ₹70 = ₹430
Maximum loss = ₹70 (if Nifty expires below 19,000)
Breakeven = 19,000 + ₹70 = 19,070
Let’s walk through an example using Nifty options:
Nifty Spot Price: 19,000
Buy 19,000 Call at ₹100
Sell 19,500 Call at ₹30
Net Premium Paid: ₹100 – ₹30 = ₹70
Nifty Expiry Level | 19,000 (or below) | 19,200 | 19,500 | 20,000 (above) |
Long Call (Buy) | 0 | ₹200 | ₹500 | ₹1,000 |
Short Call (Sell) | 0 | 0 | -₹0 | -₹500 |
Net Payoff | -₹70 | ₹130 | ₹430 | ₹430 |
If Nifty stays below 19,000: Entire premium is lost (max loss: ₹70)
If Nifty rises to 19,500: Both options are exercised; the spread between strikes is achieved minus net premium (max profit: ₹430)
Above 19,500: Profit remains capped at ₹430
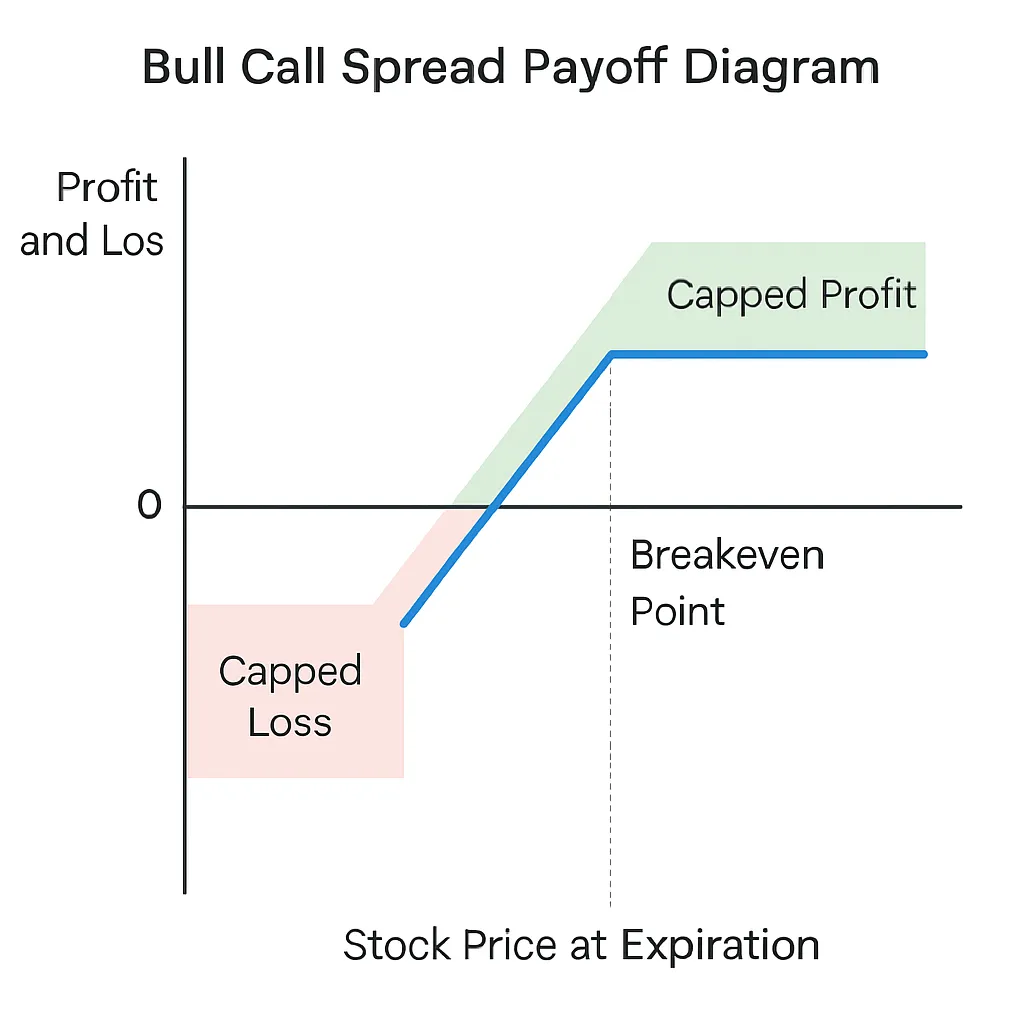
The bull call spread strategy provides a disciplined way to capture gains from moderate upward moves in a volatile market—without exposing traders to unchecked losses. By balancing risk, cost, and reward, it becomes a valuable addition to any Indian trader’s toolkit, especially in today’s unpredictable markets.
A bull call spread example: Buy a Nifty 19,000 call at ₹100, sell a Nifty 19,500 call at ₹30, net premium ₹70, maximum profit ₹430 if Nifty closes at or above 19,500.
Same as above: Using Nifty options, combine a lower and higher strike call with the same expiry; profit and loss are predefined as shown in the earlier table.
Ideal exit: When the underlying asset approaches the short call’s strike price or when most of the potential profit has been realized before expiry.
Yes, it’s profitable when the underlying rises moderately; however, profit is capped. Profits are maximized if the price settles at or above the short call’s strike.
It’s not fully loss-free, but loss is limited to the net premium paid; selecting strikes closer to spot and timing entry when volatility is high may slightly reduce risk, but complete loss elimination isn’t possible.
Discover investment portfolios that are designed for maximum returns at low risk.
Learn how we choose the right asset mix for your risk profile across all market conditions.
Get weekly market insights and facts right in your inbox
It depicts the actual and verifiable returns generated by the portfolios of SEBI registered entities. Live performance does not include any backtested data or claim and does not guarantee future returns.
By proceeding, you understand that investments are subjected to market risks and agree that returns shown on the platform were not used as an advertisement or promotion to influence your investment decisions.
"I was drawn to Wright Research due to its multi-factor approach. Their Balanced MFT is an excellent product."

By Prashant Sharma
CTO, Zydus
By signing up, you agree to our Terms and Privacy Policy
"I was drawn to Wright Research due to its multi-factor approach. Their Balanced MFT is an excellent product."

By Prashant Sharma
CTO, Zydus
Skip Password
By signing up, you agree to our Terms and Privacy Policy
"I was drawn to Wright Research due to its multi-factor approach. Their Balanced MFT is an excellent product."

By Prashant Sharma
CTO, Zydus
"I was drawn to Wright Research due to its multi-factor approach. Their Balanced MFT is an excellent product."

By Prashant Sharma
CTO, Zydus
Log in with Password →
By logging in, you agree to our Terms and Privacy Policy
"I was drawn to Wright Research due to its multi-factor approach. Their Balanced MFT is an excellent product."

By Prashant Sharma
CTO, Zydus
Log in with OTP →
By logging in, you agree to our Terms and Privacy Policy
"I was drawn to Wright Research due to its multi-factor approach. Their Balanced MFT is an excellent product."

By Prashant Sharma
CTO, Zydus
Answer these questions to get a personalized portfolio or skip to see trending portfolios.
Answer these questions to get a personalized portfolio or skip to see trending portfolios.
(You can choose multiple options)
Answer these questions to get a personalized portfolio or skip to see trending portfolios.
Answer these questions to get a personalized portfolio or skip to see trending portfolios.
Answer these questions to get a personalized portfolio or skip to see trending portfolios.
(You can choose multiple options)
Investor Profile Score
We've tailored Portfolio Management services for your profile.
View Recommended Portfolios Restart