India's Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) have emerged as transformative forces in the nation's financial ecosystem, reshaping credit intermediation through aggressive digitalization, retail segment penetration, and increasingly sophisticated underwriting methodologies. As of December 2024, the sector's cumulative credit reached ₹52 trillion, a pivotal inflection point that signals the formalization and maturation of India's shadow banking landscape. With total assets under management expected to exceed ₹60 trillion by FY26, NBFCs are no longer peripheral players in India's financial system; they have become indispensable engines of inclusive growth, democratizing access to credit for underserved populations and driving economic resilience.
The narrative of NBFC expansion is deeply intertwined with digital transformation. While traditional banks grapple with legacy infrastructure and rigid underwriting protocols, NBFCs have leveraged artificial intelligence, alternative data ecosystems, and cloud-native architectures to process loans faster, assess risk more accurately, and reach previously unbanked populations. This strategic differentiation has established NBFCs as critical bridges between formal financial infrastructure and grassroots economic participants, particularly in retail and MSME segments where their presence now dominates India's credit landscape.
The transformation of India's NBFC sector in FY25 is fundamentally defined by one phenomenon: the explosive growth of retail credit. Retail assets now constitute 58% of total NBFC lending as of December 2024, representing a historic pivot from wholesale-dominated lending models. This represents not merely a sectoral shift, but a fundamental reimagining of how NBFCs deploy capital from infrastructure and industrial financing toward personal loans, vehicle finance, microfinance, and consumer durables.
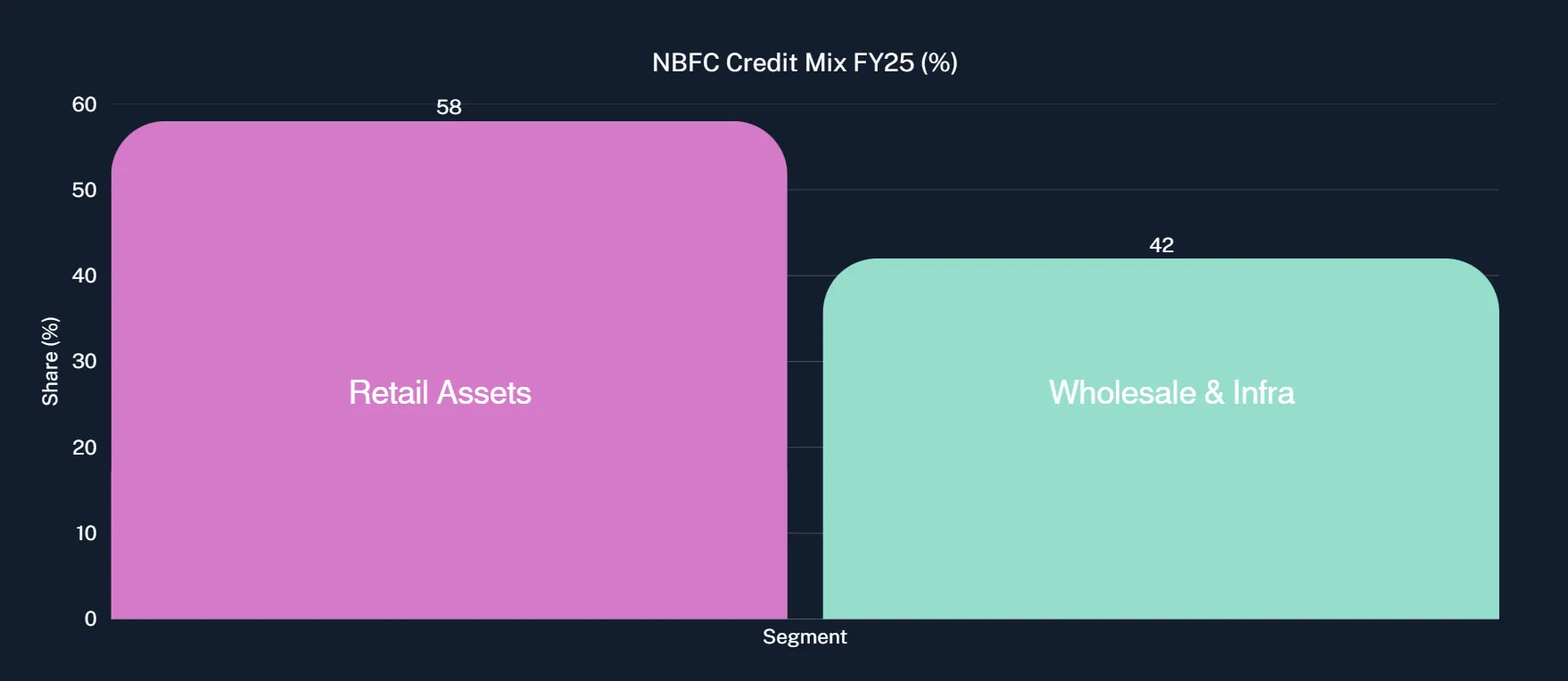
The data tells a compelling story of market democratization. The NBFC retail credit portfolio expanded at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 23% during FY23-FY24, substantially outpacing wholesale segment growth. Within this retail portfolio, vehicle loans remain the largest component, commanding 34.7% of retail lending as of March 2024, followed by gold loans, microfinance, and personal loans. This diversification across sub-segments has not only expanded the addressable market but also enhanced portfolio resilience through reduced concentration risk.
What makes this shift particularly significant is its geographical dimension. Over 51% of India's 63 million registered small businesses operate in Tier 2 and smaller cities, yet these regions have historically suffered from acute credit scarcity. NBFCs have systematically penetrated these underserved geographies through tailored products, vernacular customer support, and alternative credit assessment methodologies that banks find economically unviable. The result: retail credit has become the vehicle through which financial inclusion objectives are finally being realized at scale.
The growth trajectory remains robust despite normalization from peak expansion rates. NBFCs' retail segment is projected to expand at 16-18% annually through FY26-FY27, significantly outpacing traditional banking sector growth. This trajectory reflects underlying structural demand: first-time borrowers entering the formal credit market, rising vehicle ownership aspirations, gold lending expansion driven by jewelry consumption, and an expanding gig economy requiring flexible credit instruments.
The formalization and growth acceleration of NBFC retail segments is fundamentally enabled by digital underwriting, a technology-driven paradigm that replaces manual assessments with data-driven, AI-powered credit decisioning. This shift transcends mere operational efficiency; it represents a fundamental recalibration of credit democratization in India.
Traditional underwriting models rely on conventional metrics: CIBIL scores, income documentation, employment verification, and collateral valuation. These criteria systematically exclude millions of economically viable borrowers, gig workers, self-employed professionals, MSMEs with informal accounting, and first-time borrowers lacking credit histories. Digital underwriting obliterates this constraint by leveraging alternative data sources: GST returns, digital payment trails, utility bill payments, social media business presence, and behavioral signals.
The magnitude of this transformation cannot be overstated. NBFCs now process loan applications through 100% digital KYC protocols, e-signature frameworks, and AI-powered document verification systems that automate preliminary risk assessment and flag anomalies for human review. Generative AI models embedded in underwriting workflows cross-verify documents, calculate risk scores, and process high loan volumes without compromising accuracy enabling underwriters to focus exclusively on exceptions and complex cases.
By analyzing GST returns, fintechs and NBFCs can evaluate turnover trends, payment patterns, and business trajectories with unprecedented granularity. Lenders like LendingKart and Indifi now offer customized interest rates (15-27% range) to borrowers based on GST-derived creditworthiness assessments, fundamentally reimagining credit access for small businesses.
The practical impact is quantifiable: leading NBFCs report reduction in loan processing timelines from months to days or hours, while simultaneously reducing operational costs by 20% through strategic digital transformation. Real-time loan approvals, minimal documentation requirements, and flexible repayment schedules have become standard offerings rather than premium features.
Moreover, digital underwriting has created a virtuous cycle of regulatory compliance and risk transparency. Advanced AI credit decisioning tools now offer explainable AI (XAI) capabilities, enabling regulators to understand algorithmic decision-making processes, thereby ensuring accountability and compliance with evolving RBI norms. Every decision is traceable, auditable, and explainable positioning digital underwriting as not merely efficient but also prudentially robust.

The NBFC sector's growth has catalyzed significant regulatory formalization, fundamentally transforming the institutional architecture governing non-banking finance in India. The Reserve Bank of India's establishment of FIDC (Finance Industry Development Council) as a Self-Regulatory Organization (SRO) in April 2025 represents a watershed moment, signaling the regulator's intent to transition NBFCs from informally monitored shadow banks to formally governed financial institutions.
This regulatory evolution encompasses multiple dimensions. The RBI's Scale-Based Regulatory Framework now stratifies NBFCs into distinct layers Upper Layer (UL), Middle Layer (ML), Lower Layer (LL), and foundational categories with proportionate regulatory requirements. This differentiated approach acknowledges sector heterogeneity while ensuring prudential safeguards scale appropriately with systemic importance.
The Co-Lending Arrangements Directions 2025 represent particularly significant formalization. Effective January 2026, this unified framework governs collaborative lending between banks and NBFCs through ex-ante agreements with clearly articulated risk-sharing, revenue sharing, and operational responsibility allocation. The requirement for 10% minimum retention share per regulated entity in every individual loan ensures both parties maintain genuine financial exposure. This framework has effectively expanded co-lending beyond priority sector focus to encompass all credit segments, facilitating deeper bank-NBFC collaboration.
Capital adequacy formalization has similarly evolved. The Capital-to-Risk-Weighted Assets Ratio (CRAR) of NBFCs reached 16.8% as of September 2023, substantially exceeding the regulatory minimum of 11.5%. This robust capital positioning reflects a sector that has systematically strengthened its financial foundations through equity capital mobilization. Over the preceding 3.5 years, NBFCs raised approximately ₹70,000 crore in equity, fundamentally enhancing balance sheet resilience.
The introduction of Liquidity Coverage Ratio (LCR) requirements represents another formalization milestone, bolstering short-term resilience and reducing rollover risks that plagued the sector during previous liquidity crises. Collectively, these regulatory innovations signal the RBI's confidence in NBFC maturity while simultaneously imposing governance standards that align non-banking finance with systemic stability imperatives.
Within the retail credit universe, three segments have established clear leadership positions: vehicle loans (34.7%), gold loans, and microfinance loans collectively accounting for 56.7% of NBFC retail portfolios as of March 2024.
Vehicle loans continue commanding the largest share, benefiting from India's automotive expansion, rising consumer vehicle aspirations, and the booming used vehicle market. Two-wheeler financing, passenger vehicle loans, and commercial vehicle finance collectively represent $billions in annual disbursements. The RBI's recent assessment noted that vehicle loan prospects remain robust, buoyed by improving vehicle sales and sustained demand growth.
Gold loans have emerged as portfolio diversification engines, particularly as microfinance institutions diversify away from concentrated microcredit portfolios. The RBI's regulatory relaxation permitting NBFC-MFIs to allocate up to 40% of their portfolios to non-microfinance assets has catalyzed this shift. Lenders like Arohan Financial Services and Uttrayan Financial Services have strategically pivoted toward gold loans, leveraging tangible collateral security and countercyclical demand patterns to enhance portfolio stability.
Microfinance lending remains core to financial inclusion objectives, though increasingly complemented by diversified assets. The traditional microfinance segment serves self-employed women and small entrepreneurs with small-ticket loans (typically ₹50,000-₹300,000), but regulatory framework liberalization has enabled portfolio expansion into adjacent segments.
These three segments' collective strength reflects NBFCs' strategic positioning: they serve customer segments where traditional banks find unit economics challenging or risk profiles uncomfortable. The combination of strong collateral backing (vehicle, gold), substantial addressable populations, and established operational infrastructure positions these segments for sustained double-digit growth through FY28.
The NBFC digital transformation narrative fundamentally involves strategic partnerships with fintech innovators. Rather than viewing fintech as competitive threats, leading NBFCs have recognized collaboration as mutual growth catalysts.
These partnerships manifest across multiple operational dimensions. Digital lending platform co-creation enables NBFCs to leverage fintech technological sophistication while maintaining customer relationships and balance sheet origination. AI-based risk assessment tool development allows fintech competency in machine learning algorithms to complement NBFC customer understanding and credit expertise. API integrations for Account Aggregators, GST data, utility payments, and real-time bank statement verification streamline underwriting workflows.
Concrete examples illuminate this collaboration model. Bajaj Finance's partnership with Bharti Airtel aims to create one of India's largest digital financial platforms, combining NBFC scale with telecom distribution reach. Knight FinTech's co-lending infrastructure captures 70% market share in enabling collaborative lending platforms between banks and NBFCs. Gyde's deployment across Bajaj Finance operations reduced onboarding timelines dramatically while increasing loan approvals 50% within three months.
The magnitude of fintech-NBFC integration is evident from investment flows. Private credit inflows into Indian financial services reached a record $9 billion in H1 2025, signaling renewed global investor confidence in the stability of India's credit market and the effectiveness of fintech-NBFC collaboration models.
Despite rapid credit expansion, NBFC asset quality metrics have demonstrated remarkable resilience. The sector maintains strong Gross Non-Performing Assets (GNPA) ratios, having largely recovered from pandemic-era stress. Capital adequacy remains robust, with average CRAR positioning substantially above regulatory minimums.
The RBI's cautious attention to unsecured retail credit growth remains warranted. Unsecured personal loans expanded at 40-45% growth rates in previous years, prompting the RBI to increase risk weights on specific retail loan categories in November 2023. This regulatory tightening has effectively moderated growth in highest-risk segments while maintaining overall credit expansion momentum.
The regulatory framework itself has contributed to asset quality stabilization. Enhanced asset classification norms effective October 2022 mandate NBFCs to collect entire arrears before upgrading NPAs, establishing more conservative definitions that reduce surprise credit losses.
Systemic analysis suggests the NBFC sector has meaningfully strengthened its credit risk management capabilities. Access to alternative data, AI-powered underwriting, and granular behavioral analytics enable superior borrower screening and early warning systems. Hyper-personalization tools now send targeted reminders, nudges, and renegotiation offers based on borrower intent signals, improving collection efficiency and reducing slippage into NPAs.
The NBFC sector's future represents a synthesis of controlled growth with deepening sophistication. Credit growth projections of 13-15% through FY25-FY26 represent normalization from peak 20-23% growth, yet remain substantially above historical 11-13% averages and exceed banking sector expansion rates.
By FY28, total NBFC credit is projected to reach ₹74-77 trillion, representing portfolio tripling over a decade. This expansion will be geographically dispersed across Tier 2-4 cities, demographically distributed across first-time borrowers and gig eConomy participants, and functionally concentrated in retail segments with strong unit economics.
The institutional convergence of regulatory formalization, digital technological capacity, alternative data infrastructure, and fintech collaboration has fundamentally transformed NBFC positioning in India's financial ecosystem. No longer shadow banks operating in regulatory gray zones, NBFCs have evolved into formally regulated, technologically sophisticated, digitally native credit intermediaries that are systematically unlocking India's persistent credit frontier.
For entrepreneurs building digital wealth platforms like Bizaay, this NBFC evolution offers profound strategic implications. The formalization of credit infrastructure, establishment of clear regulatory frameworks, proliferation of API-based data ecosystems, and demonstrated success of digital-first credit delivery models have created an increasingly stable, transparent, and scalable foundation for wealth management technology innovation.
Discover investment portfolios that are designed for maximum returns at low risk.
Learn how we choose the right asset mix for your risk profile across all market conditions.
Get weekly market insights and facts right in your inbox
It depicts the actual and verifiable returns generated by the portfolios of SEBI registered entities. Live performance does not include any backtested data or claim and does not guarantee future returns.
By proceeding, you understand that investments are subjected to market risks and agree that returns shown on the platform were not used as an advertisement or promotion to influence your investment decisions.
"I was drawn to Wright Research due to its multi-factor approach. Their Balanced MFT is an excellent product."

By Prashant Sharma
CTO, Zydus
By signing up, you agree to our Terms and Privacy Policy
"I was drawn to Wright Research due to its multi-factor approach. Their Balanced MFT is an excellent product."

By Prashant Sharma
CTO, Zydus
Skip Password
By signing up, you agree to our Terms and Privacy Policy
"I was drawn to Wright Research due to its multi-factor approach. Their Balanced MFT is an excellent product."

By Prashant Sharma
CTO, Zydus
"I was drawn to Wright Research due to its multi-factor approach. Their Balanced MFT is an excellent product."

By Prashant Sharma
CTO, Zydus
Log in with Password →
By logging in, you agree to our Terms and Privacy Policy
"I was drawn to Wright Research due to its multi-factor approach. Their Balanced MFT is an excellent product."

By Prashant Sharma
CTO, Zydus
Log in with OTP →
By logging in, you agree to our Terms and Privacy Policy
"I was drawn to Wright Research due to its multi-factor approach. Their Balanced MFT is an excellent product."

By Prashant Sharma
CTO, Zydus
Answer these questions to get a personalized portfolio or skip to see trending portfolios.
Answer these questions to get a personalized portfolio or skip to see trending portfolios.
(You can choose multiple options)
Answer these questions to get a personalized portfolio or skip to see trending portfolios.
Answer these questions to get a personalized portfolio or skip to see trending portfolios.
Answer these questions to get a personalized portfolio or skip to see trending portfolios.
(You can choose multiple options)
Investor Profile Score
We've tailored Portfolio Management services for your profile.
View Recommended Portfolios Restart